Profile Estimation Experiments - the Rossler Equations
This page provides code to run profiled parameter estimation on data generated by the Rossler equations. It follows the same format as FhNEx.html and has commentary has therefore been kept to a minimum.
The Rossler equations are given by
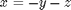
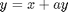
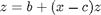
Contents
- Path Functions
- Various parameters
- Observation times
- Create paths
- Set up observations
- Fitting parameters
- Profiling optimisation control
- Setting up functional data objects
- Smooth the data
- Re-smoothing with model-based penalty
- Perform the Profiled Estimation
- Plot Smooth with Profile-Estimated Parameters
- Comparison with Smooth Using True Parameters
- Squared Error Performance
- Calculate Sample Information and Variance-Covariance Matrices
Path Functions
odefn = @rossfun1; % Function for ODE solver fn = @rossfun; % RHS function dfdy = @rossdfdy; % Derivative wrt inputs dfdp = @rossdfdp; % Derviative wrt parameters d2fdy2 = @rossd2fdy2; % Hessian wrt inputs d2fdydp = @rossd2fdydp; % Hessian wrt inputs and parameters d2fdp2 = @rossd2fdp2; % Hessian wrt parameters. d3fdy3 = @rossd3fdy3; % Third derivative wrt inputs. d3fdy2dp = @rossd3fdy2dp; % Third derivative wrt intputs, inputs and pars. d3fdydp2 = @rossd3fdydp2; % Third derivative wrt inputs, pars and pars.
Various parameters
y0 = [1.13293; -1.74953; 0.02207]; % Initial conditions pars = [0.2; 0.2; 3]; % Parameters sigma = 0.5; % Noise Level jitter = 0.2; % Perturbation for starting ppars = pars + jitter*randn(length(pars),1); % of parameter estimates disp(ppars')
0.3969 0.2470 3.2257
Observation times
tspan = 0:0.05:20; % Observation times obs_pts{1} = 1:length(tspan); % Which components are observed at obs_pts{2} = 1:length(tspan); % which observation times. obs_pts{3} = 1:length(tspan); tfine = 0:0.05:20; % Times to plot solutions
Create paths
odeopts = odeset('RelTol',1e-13);
[full_time,full_path] = ode45(odefn,tspan,y0,odeopts,pars);
[plot_time,plot_path] = ode45(odefn,tfine,y0,odeopts,pars);
Set up observations
tspan = cell(1,size(full_path,2)); path = tspan; for(i = 1:length(obs_pts)) tspan{i} = full_time(obs_pts{i}); path{i} = full_path(obs_pts{i},i); end % add noise noise_path = path; for(i = 1:length(path)) noise_path{i} = path{i} + sigma*randn(size(path{i})); end % and set wts wts = []; if(isempty(wts)) % estimate wts if not given for(i = 1:length(noise_path)) wts(i) = 1./sqrt(var(noise_path{i})); end end
Fitting parameters
lambda = 1e4; % Smoothing for model-based penalty lambda = lambda*wts; lambda0 = 1; % Smoothing for 1st-derivative penalty nknots = 401; % Number of knots to use. nquad = 5; % No. between-knots quadrature points. norder = 3; % Order of B-spline approximation
Profiling optimisation control
lsopts_out = optimset('DerivativeCheck','off','Jacobian','on',... 'Display','iter','MaxIter',1000,'TolFun',1e-8,'TolX',1e-10); % Other observed optimiation control lsopts_other = optimset('DerivativeCheck','off','Jacobian','on',... 'Display','iter','MaxIter',1000,'TolFun',1e-14,'TolX',1e-14,... 'JacobMult',@SparseJMfun); % Optimiation control within profiling lsopts_in = optimset('DerivativeCheck','off','Jacobian','on',... 'Display','off','MaxIter',1000,'TolFun',1e-14,'TolX',1e-14,... 'JacobMult',@SparseJMfun);
Setting up functional data objects
% set up knots range = [min(full_time),max(full_time)]; % range of observations knots_cell = cell(size(path)); % knots for each basis knots_cell(:) = {linspace(range(1),range(2),nknots)}; % set up bases basis_cell = cell(1,length(path)); % Create cell arrays. Lfd_cell = cell(1,length(path)); nbasis = zeros(length(path),1); bigknots = knots_cell{1}; % bigknots used for quadrature points nbasis(1) = length(knots_cell{1}) + norder - 2; for(i = 2:length(path)) bigknots = [bigknots knots_cell{i}]; nbasis(i) = length(knots_cell{i}) + norder -2; end quadvals = MakeQuadPoints(bigknots,nquad); % Create simpson's rule % quadrature points and values for(i = 1:length(path)) basis_cell{i} = MakeBasis(range,nbasis(i),norder,... % create bases knots_cell{i},quadvals,1); % with quadrature Lfd_cell{i} = fdPar(basis_cell{i},1,lambda0); % pts attatched end
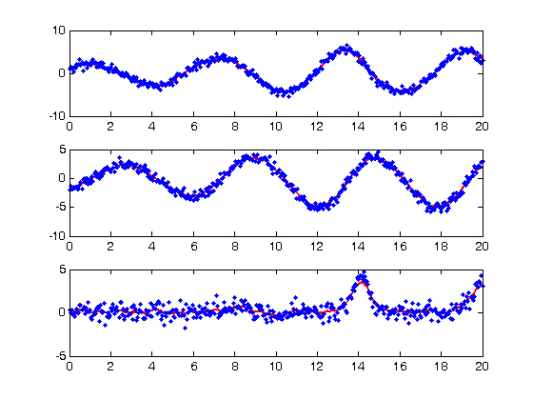
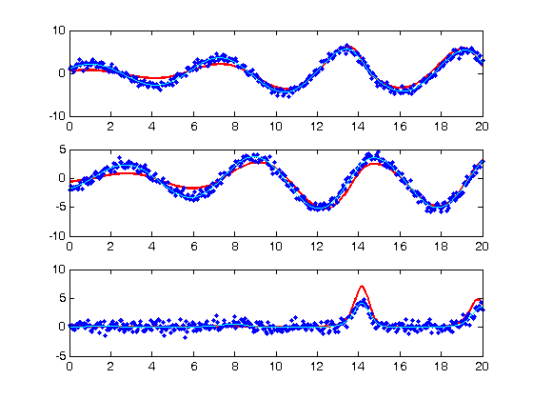
Smooth the data
DEfd = smoothfd_cell(noise_path,tspan,Lfd_cell); coefs = getcellcoefs(DEfd); devals = eval_fdcell(tfine,DEfd,0); for(i = 1:length(path)) subplot(length(path),1,i); plot(tfine,devals{i},'r','LineWidth',2); hold on; plot(tspan{i},noise_path{i},'b.'); hold off; end
Re-smoothing with model-based penalty
% Call the Gauss-Newton solver [newcoefs,resnorm2] = lsqnonlin(@SplineCoefErr,coefs,... [],[],lsopts_other,basis_cell,noise_path,tspan,wts,lambda,fn,... dfdy,[],[],[],ppars); tDEfd = Make_fdcell(newcoefs,basis_cell); % Plot results along with exact solution devals = eval_fdcell(tfine,tDEfd,0); for(i = 1:length(path)) subplot(length(path),1,i); plot(tfine,devals{i},'r','LineWidth',2); hold on; plot(tspan{i},noise_path{i},'b.'); plot(plot_time,plot_path(:,i),'c'); hold off end
Norm of First-order
Iteration Func-count f(x) step optimality CG-iterations
0 1 229369 1.57e+004
1 2 12060.1 4.99116 1.6e+003 14
2 3 4973.78 10 1.51e+003 165
3 4 1151.34 13.1452 937 160
4 5 812.383 0.33509 37.6 26
5 6 812.383 10.8313 37.6 306
6 7 732.104 2.70784 206 0
7 8 732.104 5.41567 206 215
8 9 685.263 1.35392 385 0
9 10 660.713 2.70784 226 222
10 11 625.084 0.0555431 25.8 11
11 12 622.832 2.70784 214 294
12 13 601.016 0.0392269 26 10
13 14 598.501 0.676959 29.7 292
14 15 597.705 0.570007 22.6 250
15 16 597.652 0.00227555 0.993 13
16 17 597.609 0.198483 15.9 416
17 18 597.606 0.000391115 0.371 10
18 19 597.605 0.0336477 0.107 556
19 20 597.605 0.00760102 0.00435 508
20 21 597.605 0.00188402 0.00225 547
21 22 597.605 0.00040236 6.65e-005 524
22 23 597.605 0.00011288 0.000161 555
23 24 597.605 2.54135e-005 1.63e-005 558
24 25 597.605 7.69495e-006 1.26e-005 550
25 26 597.605 1.79362e-006 2.18e-006 396
Optimization terminated: relative function value
changing by less than OPTIONS.TolFun.
Perform the Profiled Estimation
[newpars,newDEfd_cell] = Profile_GausNewt(ppars,lsopts_out,DEfd,fn,... dfdy,dfdp,d2fdy2,d2fdydp,lambda,noise_path,tspan,wts,... [],[],[],[],lsopts_in); disp(newpars);
Iteration steps Residual Improvement Grad-norm parameters
1 1 256.672 0.513038 265 0.1563 0.26934 3.0183
2 1 198.494 0.226661 12.5 0.19974 0.2008 2.9388
3 1 197.588 0.00456608 0.695 0.19932 0.20653 3.034
4 1 197.587 4.43208e-006 0.00502 0.19943 0.206 3.0335
5 1 197.587 6.47181e-009 0.00083 0.19943 0.20604 3.0337
0.1994
0.2060
3.0337
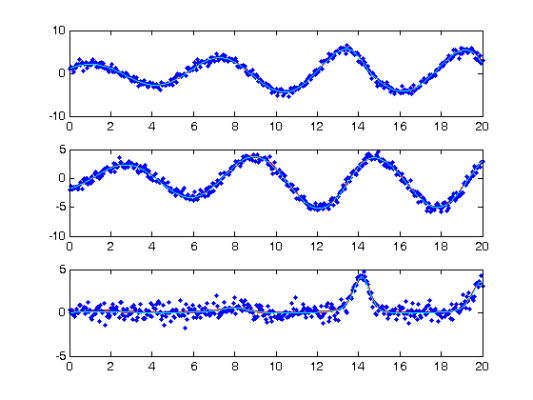
Plot Smooth with Profile-Estimated Parameters
devals = eval_fdcell(tfine,newDEfd_cell,0); for(i = 1:length(path)) subplot(length(path),1,i) plot(tfine,devals{i},'r','LineWidth',2); hold on; plot(tspan{i},noise_path{i},'b.'); plot(plot_time,plot_path(:,i),'c'); hold off end
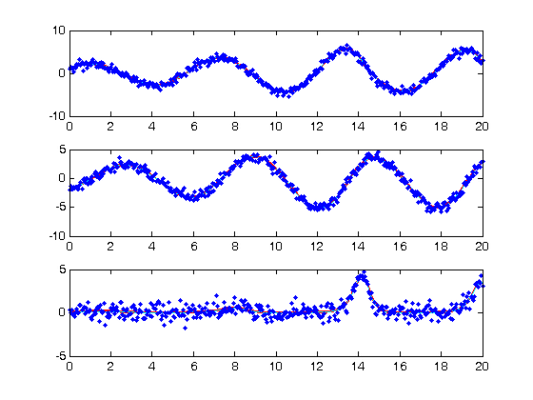
Comparison with Smooth Using True Parameters
coefs = getcellcoefs(DEfd); % Starting coefficient estimates [truecoefs,resnorm4] = lsqnonlin(@SplineCoefErr,coefs,[],[],... lsopts_other,basis_cell,noise_path,tspan,wts,lambda,fn,dfdy,... [],[],[],pars); trueDEfd_cell = Make_fdcell(truecoefs,basis_cell); devals = eval_fdcell(tfine,trueDEfd_cell,0); for(i = 1:length(path)) subplot(length(path),1,i) plot(plot_time,plot_path(:,i),'c') plot(tfine,devals{i},'r','LineWidth',2); hold on; plot(plot_time,plot_path(:,i),'c'); plot(tspan{i},noise_path{i},'b.'); hold off; end
Norm of First-order
Iteration Func-count f(x) step optimality CG-iterations
0 1 199278 1.83e+004
1 2 4085.02 3.58379 1.01e+003 10
2 3 377.193 2.49177 232 38
3 4 220.163 2.33239 129 140
4 5 214.834 2.92018 747 301
5 6 199.351 0.0321855 18 13
6 7 198.667 0.477268 8.21 327
7 8 198.5 0.505036 17.4 515
8 9 198.49 0.000870897 0.338 14
9 10 198.489 0.00713026 0.0203 221
10 11 198.489 0.0119639 0.00803 541
11 12 198.489 0.000835713 0.000177 448
12 13 198.489 0.000191154 0.0001 603
13 14 198.489 9.78293e-007 4.89e-006 48
14 15 198.489 4.39558e-006 1.9e-006 603
15 16 198.489 2.58483e-009 4.11e-007 21
Optimization terminated: relative function value
changing by less than OPTIONS.TolFun.
Squared Error Performance
% Squared error for estimated parameters newpreds = eval_fdcell(tspan,newDEfd_cell,0); new_err = cell(length(newpreds)); for(i = 1:length(path)) new_err{i} = wts(i)*(newpreds{i} - noise_path{i}).^2; end new_err = mean(cell2mat(new_err)); % Squared error for true parameters truepreds = eval_fdcell(tspan,trueDEfd_cell,0); true_err = cell(length(truepreds)); for(i = 1:length(path)) true_err{i} = wts(i)*(truepreds{i} - noise_path{i}).^2; end true_err = mean(cell2mat(true_err)); % print out a comparsion disp([new_err true_err]);
0.1642 0.1643
Calculate Sample Information and Variance-Covariance Matrices
% Hessian of squared error with respect to parameters d2Jdp2 = make_d2jdp2(newDEfd_cell,fn,dfdy,dfdp,d2fdy2,d2fdydp,d2fdp2,... d3fdy3,d3fdy2dp,d3fdydp2,tspan,lambda,newpars,[],wts,... [],[],[],noise_path) % Second derivatives with respect to parameters and observations d2JdpdY = make_d2jdpdy(newDEfd_cell,fn,dfdy,d2fdy2,d3fdy3,dfdp,d2fdydp,d3fdy2dp,... tspan,lambda,newpars,[],wts,[],[],[],noise_path); % Resulting derivative of parameters with respect to observations dpdY = -d2Jdp2\d2JdpdY; % Variance of observations: S = make_sigma(DEfd,tspan,noise_path,0); % Resulting parameter covariance matrix: Cov = dpdY*S*dpdY'
d2Jdp2 =
1.0e+004 *
3.4315 -0.4993 -0.0084
-0.4993 0.4205 -0.0785
-0.0084 -0.0785 0.0272
Cov =
0.0000 0.0000 0.0002
0.0000 0.0003 0.0009
0.0002 0.0009 0.0037